+86 13827272341
Release date:2025-07-31
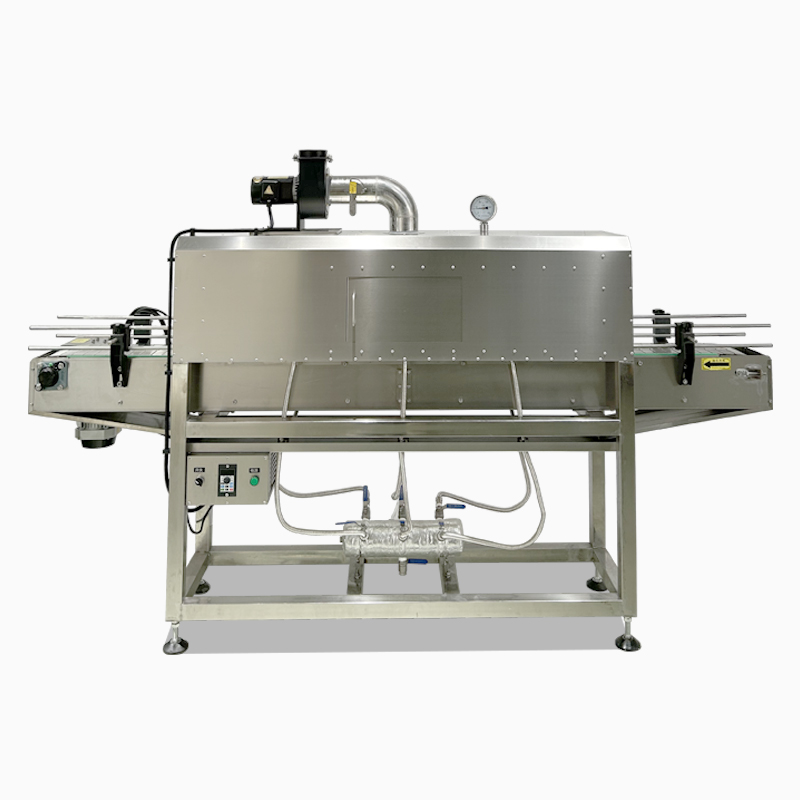
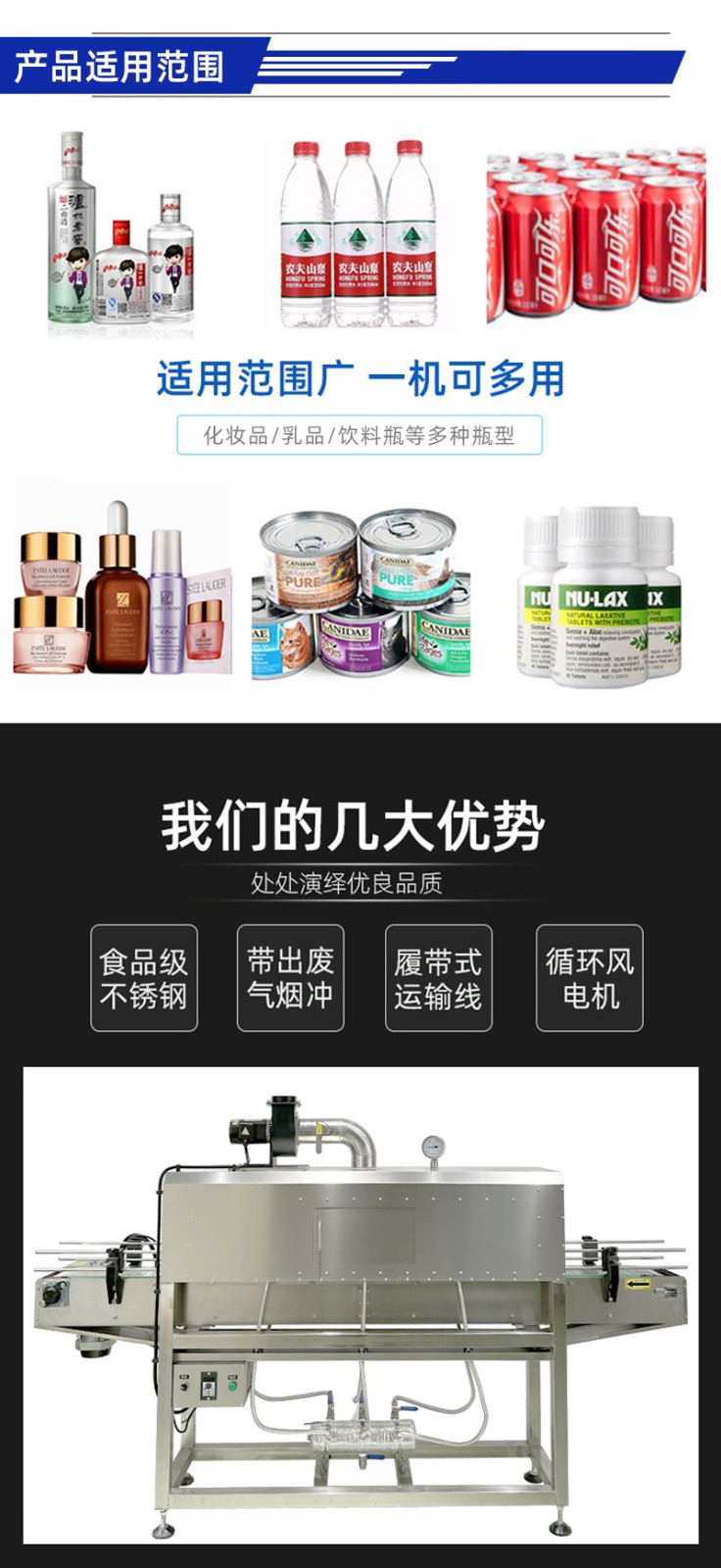
Steam shrink machines, characterized by uniform steam heating and stable shrinking effects, are suitable for multiple industries with high requirements for packaging aesthetics and sealing performance. Meanwhile, due to their working environment of moist heat steam, they also have specific requirements for the material and performance of shrink films. The detailed explanations are as follows:
I. Industries Suitable for Steam Shrink Machines
The core advantage of steam shrink machines lies in using moist heat steam to uniformly shrink shrink films, making them particularly suitable for scenarios requiring "wrinkle-free, tight fit, and low-temperature shrinking". The main applicable industries include:
Food and Beverage Industry
Bottled/canned products: Such as mineral water, purified water, carbonated drinks, fruit juice, beer, and dairy products (yogurt, milk), etc. They are used for label shrinking (to make bottle labels fit tightly) or multi-bottle collective packaging (e.g., outer shrink film packaging for 6-bottle beverage packs).
Bagged/boxed food: Such as instant noodles, snacks, frozen food, etc. Shrink film packaging is used for moisture-proofing, dust-proofing, and improving the neatness of appearance.
Features: The food industry has high requirements for packaging safety. The low-temperature characteristic of steam shrinking (lower temperature compared to hot air shrink machines) can reduce the impact of high temperature on food. Additionally, the tight fit of shrink films avoids secondary pollution.
Daily Chemical and Cosmetics Industry
Bottled/canned products: Such as shampoo, body wash, skin care products, detergents, toothpaste, etc. They are used for shrinking bottle labels (especially for special-shaped bottles, as steam can uniformly wrap curved surfaces) or combined packaging (e.g., outer shrinking of skin care sets).
Features: Daily chemical products focus on packaging aesthetics. Steam shrinking can prevent film wrinkling and whitening, maintain clear label patterns, and enhance product quality.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Industry
Pharmaceutical packaging: Such as bottled tablets, capsules, oral liquids, and medical devices (e.g., syringes, infusion sets), etc. They are used for label shrinking or sterile packaging (to reduce bacterial invasion after the shrink film is sealed).
Features: The pharmaceutical industry has strict requirements for packaging sealing performance and cleanliness. The uniformity of steam shrinking ensures full adhesion of the film, and the equipment is easy to clean, complying with GMP standards.
Electronics and Hardware Industry
Small electronic products: Such as earphones, chargers, batteries, electronic components, etc. Shrink film packaging is used for scratch resistance and anti-oxidation.
Hardware parts: Such as small tools, screws, accessories, etc. Shrink films can fix scattered parts, facilitating transportation and storage.
Features: Steam shrinking causes no high-temperature damage to products (avoiding aging of electronic components due to high temperature), and the film has strong tightness after shrinking, protecting products from external impact.
Wine and Gift Industry
Wine packaging: Such as shrinking labels on bottles of white wine, red wine, and foreign wine (especially glass bottles, as steam can adapt to the heat resistance of glass) or shrinking the outer layer of gift boxes (to enhance the grade of gifts).
Gift sets: Such as tea gift boxes, health product gift boxes, etc. Shrink films can fix the structure of gift boxes, prevent dust and moisture, and maintain packaging integrity.
II. Requirements of Steam Shrink Machines for Shrink Films
The heating medium of steam shrink machines is moist heat steam (with a temperature usually ranging from 100-150℃), which is different from the dry heat environment of hot air shrink machines. Therefore, there are specific requirements for the material and performance of shrink films, mainly including:
Material Compatibility
Prioritize low-temperature shrink films: Such as POF (polyolefin heat shrink film) and PE (polyethylene heat shrink film). These films can achieve sufficient shrinking at 100-130℃, adapting to the medium and low temperature environment of steam. Avoid high-temperature shrink films (e.g., some PVC films, which require temperatures above 150℃ and tend to shrink incompletely or deform in a steam environment).
Moist heat resistance: The film should shrink stably in a moist heat environment without dissolving or cracking. The moist heat resistance of POF and PE films is better than that of PVC (PVC may release harmful substances when exposed to high-temperature steam and is prone to embrittlement).
Shrinkage Rate and Balance
Moderate shrinkage rate: The transverse shrinkage rate usually needs to be 30%-50%, and the longitudinal shrinkage rate 20%-40% (adjusted according to product size). This ensures the film can tightly wrap the product. A too low shrinkage rate will result in loose fit, while a too high rate will easily cause wrinkling.
Balanced transverse and longitudinal shrinkage: The difference between transverse and longitudinal shrinkage rates should not be too large (generally not exceeding 10%); otherwise, "lateral shrinkage" or "longitudinal stretching" will occur, leading to packaging deformation.
Temperature Resistance Stability
The film should shrink stably at steam temperature (100-150℃) without melting, abnormal odor, or precipitates (especially when in contact with food/pharmaceuticals, it must comply with safety standards).
Low-temperature shrinking characteristic: Prevent the film from shrinking in advance at temperatures lower than steam temperature (e.g., shrinking at room temperature) or failing to shrink at temperatures higher than steam temperature (requiring high-temperature triggering).
Physical Performance Requirements
Transparency and glossiness: After shrinking, the film surface should be free of fogging and bubbles, maintaining high transparency (e.g., POF films have a transparency of over 90% after shrinking) to ensure product labels or appearance are clearly visible.
Flexibility and strength: After shrinking, the film should have certain toughness (tear resistance) to avoid damage due to collision during transportation. Meanwhile, the surface should be smooth without burrs to prevent scratching the product.
Thickness uniformity: The thickness deviation of the film should be ≤5% (e.g., for a designed thickness of 20μm, the actual deviation should not exceed 1μm). Otherwise, excessive local thickness will cause incomplete shrinking, and excessive thinness will easily lead to cracking.
Industry Compliance
Food/pharmaceutical industry: Shrink films must comply with food contact material standards (e.g., FDA, GB 4806.7) and pharmaceutical packaging material standards (e.g., YBB standards), with no release of harmful substances such as plasticizers and heavy metals.
Environmental requirements: Some industries (e.g., European and American markets) require shrink films to be degradable (e.g., PBAT/PLA composite films) or recyclable, meeting environmental certifications (e.g., compostable certification).
Heat-sealing Performance (for packaging requiring sealing)
If the shrink film needs heat-sealing (e.g., sealing of collective packaging), it should have good heat-sealing strength (≥1.5N/15mm) to ensure no leakage at the seal. Additionally, the heat-sealing temperature should match the steam shrinking temperature to avoid seal cracking during shrinking after heat-sealing.