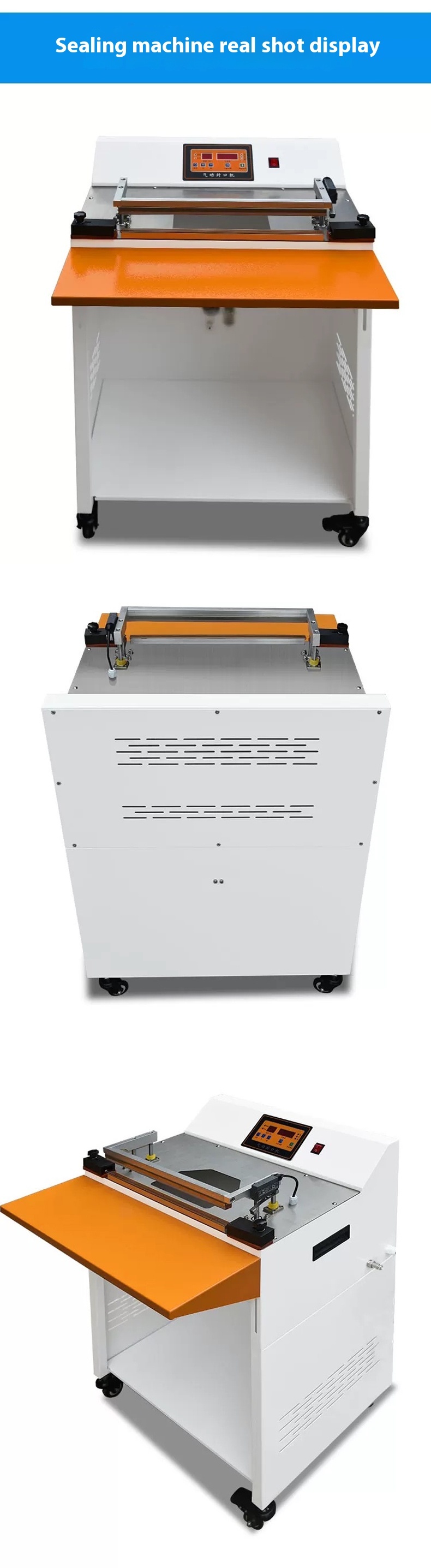
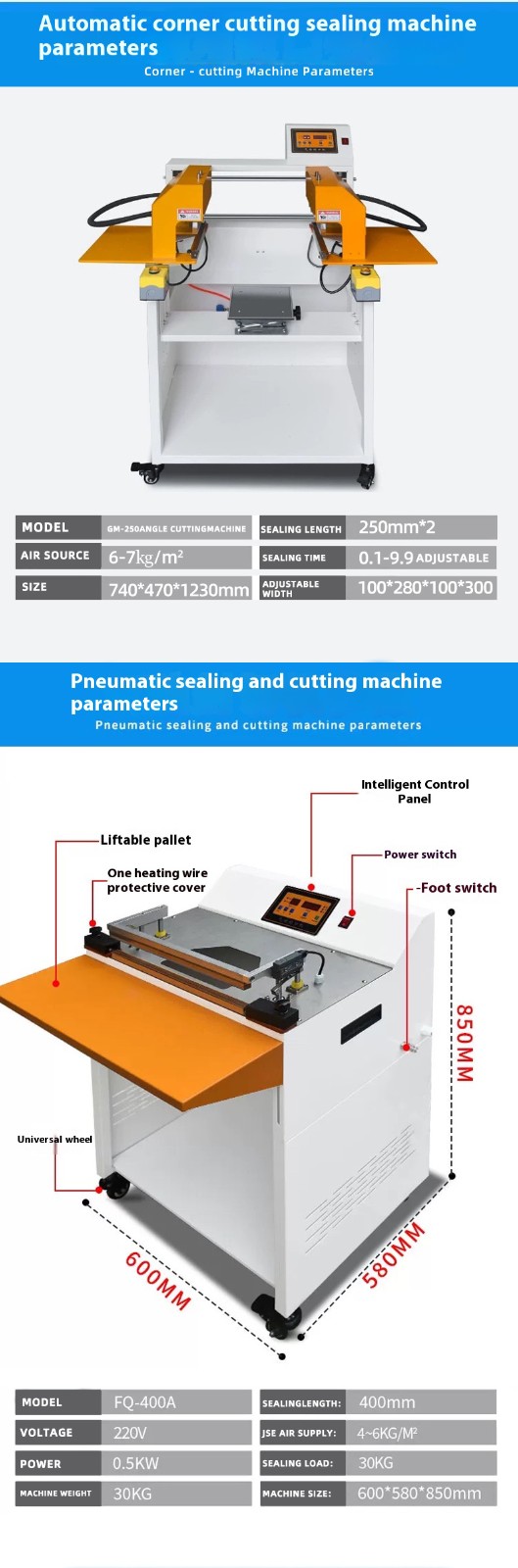
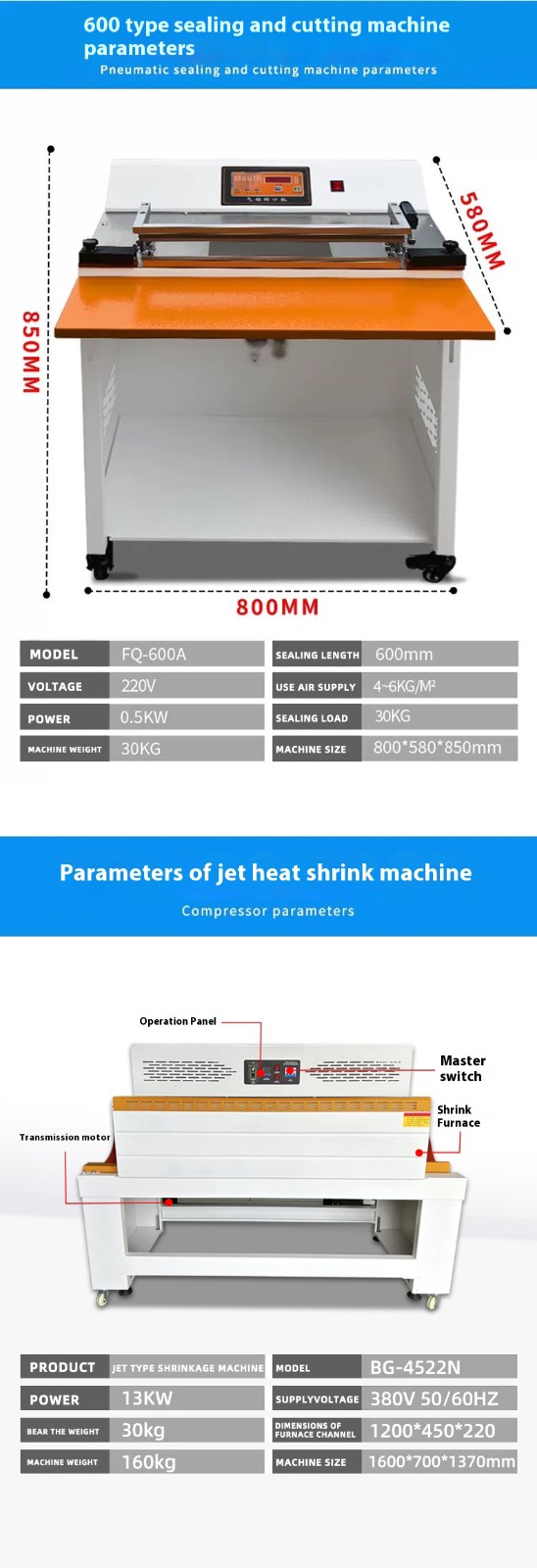
The working efficiency of a pneumatic sealing, corner-cutting, and heat shrinkage machine is influenced by multiple factors such as equipment performance, parameter settings, product specifications, and operational environment. Its core efficiency can be analyzed from the following aspects:
- Theoretical Efficiency: Mainstream models can process 10–30 pieces per minute (depending on product size and packaging complexity). For example:
- Small daily necessities (e.g., toothpaste): 20–30 pieces/min.
- Large products (e.g., cartons): 10–15 pieces/min.
- Actual Efficiency: Affected by manual feeding speed, equipment debugging time, and consumable replacement frequency, actual capacity is typically 80–90% of the theoretical value. Highly automated models (e.g., with fully automatic feeding systems) can approach theoretical capacity more closely.
- Multi-station integrated design: Feeding, sealing, corner-cutting, and heat shrinkage can be completed synchronously, reducing intermediate delays. For example, sealing and corner-cutting actions driven by a pneumatic system can achieve a single cycle in 2–5 seconds, significantly improving efficiency.
- High-end models support uninterrupted consumable replacement (e.g., automatic film splicing technology), avoiding downtime due to film changes and further enhancing continuous operation capabilities.
- Pneumatic system power: Stable air compressor pressure (typically ≥0.6MPa) and fast cylinder response (action time <1 second) ensure rapid and precise sealing/corner-cutting.
- Heat shrinkage system efficiency:
- Heating furnace warm-up speed (e.g., <5 minutes from room temperature to 200°C).
- Uniform hot air circulation (temperature difference ≤±5°C) directly impacts shrinkage speed; high-efficiency models can complete film shrinkage in 3–5 seconds.
- Intelligent control system: Microcomputers can preset multiple parameter groups (e.g., save 10–20 product recipes), reducing model changeover time to 5–10 minutes without re-debugging.
- Product size diversity: Frequent switching of product sizes requires adjusting sealing positions, corner-cutting tools, and conveying speed, potentially reducing efficiency. Models with quick-change mold components (e.g., adjustable sealing molds) can minimize adjustment time.
- Packaging material properties: Thick films or materials requiring high shrinkage temperatures (e.g., PET-G film) need higher temperatures and longer shrinkage times, possibly increasing processing time per piece by 1–2 seconds.
- Manual intervention frequency: Semi-automatic models require manual feeding, with efficiency ~60–70% of fully automatic models; fully automatic models (e.g., with robotic gripping) enable unmanned operation, significantly improving efficiency.
- Equipment maintenance status: Regular cleaning of heating elements and lubrication of pneumatic components reduce downtime (e.g., 5–10 minutes per shutdown due to sticky sealing blades).
- Vision inspection system: Real-time monitoring of sealing quality and corner-cutting precision, automatically rejecting 不合格 products to reduce manual sampling time.
- Production line integration: Docking with upstream filling lines and downstream boxing lines to form a fully automated production line, eliminating inter-process waiting time.
- Preset optimal sealing temperature (typically 180–250°C), heat shrinkage temperature (150–220°C), and conveying speed (0.5–3m/min) based on film type (e.g., PE, PVC, POF) and product size to avoid reprocessing due to incorrect parameters.
- Establish regular maintenance plans (e.g., daily cleaning of sealing blades, weekly inspection of pneumatic pipeline airtightness), reducing failure rates. Statistics show regular maintenance can reduce downtime by 30–50%.